Article / Research Article
Medicea Medica Srl (PMI Innovativa); Maritime Medical Associates; GDM Livorno Gente di Mare. Italy.
Claudio Bencini, MD, FICS, FBHS, MSD-IMM.
Medicea Medica Srl (PMI Innovativa); Maritime Medical Associates;
GDM Livorno Gente di Mare.
Italy.
30 September 2025 ; 15 October 2025
Rapid diagnosis and early treatment of Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) remain challenging outside hospital environments. We implemented a pragmatic Point-of-Care Testing and Therapy (POCT-T) model combining smartphone electrocardiography KardiaMobile ECG (KM-ECG) and semi-quantitative lateral-flow immunoassays (LFIA) for cardiac troponin, tailored for maritime and other remote operations.
We describe the technology stack (KardiaMobile ECG and LFIA troponin), summarize published accuracy data, and propose an operational workflow to reduce time-to-diagnosis and time-to-treatment. Literature was reviewed on smartphone ECG performance for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), prehospital ECG transmission programs, and rapid LFIA troponin tests. Key endpoints were diagnostic accuracy and estimated time intervals from symptom onset to first ECG, biomarker result, activation decision, and reperfusion.
Sequential smartphone ECG leads (≥2 including a precordial position) showed high sensitivity and specificity for STEMI detection in a prospective study, whereas single-lead alone was modestly sensitive (De la Torre Hernández et al., 2021).
LFIA troponin provides a qualitative/semi-quantitative result in ~10–15 minutes, with utility growing beyond the first hours from symptom onset but lower sensitivity than high-sensitivity quantitative assays (Collinson & Gaze, 2020; Roche Diagnostics, 2025; Mohammadinejad et al., 2024).
Prehospital ECG transmission programs consistently reduce door-to-device times and facilitate earlier activation of PCI pathways (Moxham et al., 2024).
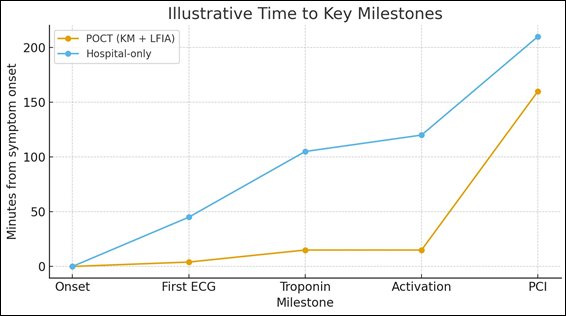
A combined KM+LFIA workflow can anticipate diagnostic confirmation by tens of minutes compared with hospital-only pathways, potentially shortening total ischemic time.
In resource-limited or remote environments, coupling smartphone ECG with rapid LFIA troponin is feasible, low-cost, and operationally impactful. This POCT-T approach may accelerate early antiplatelet therapy and targeted evacuation while preserving clinical oversight via teleconsultation (Byrne et al., 2023; Gulati et al., 2021).
Acute Coronary Syndrome; ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction; Point-Of-Care Testing; Smartphone ECG; Lateral-Flow Immunoassay; Maritime Medicine.
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) mandates fast, accurate diagnosis and timely reperfusion because ischemic time correlates with mortality and infarct size (Byrne et al., 2023). Guidelines emphasize early ECG acquisition, troponin testing with high-sensitivity assays, and streamlined pathways to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) (Byrne et al., 2023; Gulati et al., 2021).
However, in remote contexts (e.g., vessels at sea, rural islands, austere environments) logistical delays are common and diagnostic infrastructure is limited. To bridge this gap, we designed a Point-of-Care Testing and Therapy (POCT-T) model that couples immediate smartphone ECG acquisition with a rapid troponin LFIA at the first medical contact (FMC), supported by telemedicine.
POCT-T is defined as the integrated use of bedside diagnostics and immediate therapy when indicated, guided by remote specialist input. For ECG, we employed a smartphone-based device (KardiaMobile; AliveCor, Inc.) capable of single-lead recordings and, in the 6-lead version, limb-lead vectors (I, II, III, aVR, aVL, aVF) (AliveCor, 2025).
For biomarkers, we utilized qualitative/semi-quantitative lateral-flow immunoassays (LFIA) for cardiac troponin T/I (e.g., Roche TROP T sensitive; Accu-Tell) yielding visual bands with a fixed cut-off (Collinson & Gaze, 2020; Roche Diagnostics, 2025; Accu-Tell (n.d)).
Both tools are handheld, battery-operated or instrument-free, and suited to maritime conditions (limited power, variable temperatures, and telecommunication constraints).
Operational workflow: (De la Torre Hernández et at., 2021) symptom triage and immediate KM ECG; (Collinson & Gaze, 2020) LFIA troponin from peripheral blood; (Roche Diagnostics, 2025) secure transmission of ECG PDF/photo and troponin result to a cardiology consultant; (Mohammadinejad et al., 2024) early pharmacotherapy when indicated (e.g., aspirin) and prioritized evacuation or direct transfer activation; (Moxham et al., 2024) documentation and quality control logs for training and audit (Byrne et al., 2023; Gulati et al., 2021).
KardiaMobile provides rapid ECG acquisition (≈30–120 s) and, when ≥2 sequential lead positions including a precordial lead are obtained, achieves high sensitivity and specificity for STEMI detection in patients with confirmed events (De la Torre Hernández et al., 2021).
The system includes a rhythm-screening algorithm, but STEMI identification relies on clinician interpretation of ST-segment deviations; the shortened time to first ECG and ability to transmit tracings are key advantages in prehospital contexts (Moxham et al., 2024).
The 6-lead version enhances vector information versus single-lead and has shown qualitative/quantitative equivalence to standard limb leads for arrhythmia assessment (AliveCor, 2025).
LFIA cassette tests deliver a visible band within 10–15 minutes using whole blood, plasma, or serum, requiring no instrument and minimal operator training (Collinson & Gaze, 2020; Roche Diagnostics, 2025).
They are suitable where high-sensitivity quantitative analyzers are impractical; however, LFIA assays typically have higher decision thresholds and reduced sensitivity among very early presenters (Collinson & Gaze, 2020; Mohammadinejad et al., 2024; Accu-Tell (n.d)).
Manufacturer documentation and independent evaluations detail intended use, sample types, and performance characteristics for troponin T and I LFIA kits (Collinson & Gaze, 2020; Roche Diagnostics, 2025; Accu-Tell (n.d)).
Early administration of antiplatelet therapy in suspected ACS reduces mortality and reinfarction risk. Aspirin has robust evidence for early benefit when given at first medical contact, including prehospital settings (ISIS-2 (Second International Study of Infarct Survival), 1988; Byrne et al., 2023; Gulati et al., 2021).
LMWHs (e.g., enoxaparin) provide effective anticoagulation in ACS and have demonstrated reductions in ischemic endpoints compared with unfractionated heparin in non-ST-elevation settings, with acceptable bleeding profiles when appropriately dosed (Seppälä et al., 1997; Antman et al., 1999; Byrne et al., 2023).
Within a POCT-T framework, initiating aspirin (in absence of contraindications) after an ischemic ECG pattern or high clinical suspicion, and considering LMWH per guideline-directed indications, can advance definitive care by ‘starting the clock’ on evidence-based therapy even before hospital arrival, while maintaining teleconsultant oversight (Byrne et al., 2023; Gulati et al., 2021).
Prehospital ECG transmission programs reduce door-to-device/balloon time and first-medical-contact-to-device intervals by enabling earlier activation of PCI teams (Moxham et al., 2024).
Guidelines target door-to device ≤90 minutes for STEMI and emphasize minimizing total ischemic time from symptom onset (Byrne et al., 2023; Gulati et al., 2021).
Registry medians for symptom-to-balloon often approximate 180–230 minutes in contemporary systems, indicating major delays pre-arrival or during in-hospital queueing (Moxham et al., 2024; Gulati et al., 2021).
A KM+LFIA workflow can anticipate first diagnostic confirmation (ECG within minutes; LFIA ≈15 minutes), potentially shifting activation earlier and reducing total ischemic time, especially where distances are significant (e.g., at sea).
- Earlier initiation of guideline-directed therapy (aspirin ± LMWH) at FMC when clinically indicated.
- Faster diagnostic confidence by combining ECG patterns with biomarker corroboration (LFIA troponin) within ~15 minutes (Collinson & Gaze, 2020; Moxham et al., 2024).
- Parallelization of care: triage, ECG, troponin, and teleconsultation proceed concurrently, shortening time-to-activation of PCI pathways.
- Potential reduction in total ischemic time compared with hospital-only pathways, which accumulate transport and triage delays (Moxham et al., 2024; Byrne et al., 2023; Gulati et al., 2021).
- Feasibility and scalability in remote settings with minimal equipment and training requirements.
LFIA assays are less sensitive than high-sensitivity quantitative platforms and can be negative in very early presenters; diagnostic pathways must preserve serial testing and clinical judgment (Collinson & Gaze, 2020; Mohammadinejad et al., 2024).
Smartphone ECG STEMI detection depends on proper lead placement and interpretation; automatic rhythm algorithms do not diagnose MI (De la Torre Hernández et al., 2021; AliveCor, 2025).
Connectivity constraints at sea may delay teleconsultation; contingency plans and checklists are essential.
A combined POCT-T strategy using smartphone ECG and rapid LFIA troponin is feasible and operationally impactful for maritime and other remote settings. By shifting diagnostic confirmation to the point of first contact, it may reduce time to activation and reperfusion, complementing guideline-directed care pathways (Moxham et al., 2024; Byrne et al., 2023; Gulati et al., 2021).
Future work should quantify outcome benefits and define standardized training and quality metrics for remote implementations.
Dr. Claudio Bencini is Founder and Legal Representative of Medicea Medica Srl (PMI Innovativa). Medicea Medica Srl has no commercial relationship with AliveCor, Roche Diagnostics, Accu-Tell or other manufacturers of the devices referenced in this work. All devices and consumables cited herein (smartphone ECG and LFIA troponin kits) were procured through standard commercial channels without support from the manufacturers. The authors declare no other conflicts of interest related to the content of this article.
This work received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors. All costs were covered by the authors’ institutions as part of routine quality improvement and training activities.
This article describes an implementation framework and does not include individual patient-level data or images. No intervention beyond guideline-directed standard of care was performed. Accordingly, formal ethics committee approval was not required. If case vignettes or anonymized ECG excerpts are included in future versions, written informed consent will be obtained and the report will conform to the Declaration of Helsinki.
No datasets were generated or analyzed for this study. Operational checklists, training materials and example workflows are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
- De la Torre Hernández, J. M., Ongay, A. G., Villarroel, T. B., Lizarbe, S. G., Fernandez, G. V., Villa, S. C., De Tapia Majado, B., González, M. L., Saint Quirico, M. M., Lozano, D. S., Rubio, I. C., Ceña, J. S., García-Camarero, T., Enríquez, S. G., Entem, F. R., García, V. E., Olalla, J. J., & Zueco, J. (2021). Diagnostic sensitivity of a smartphone-based electrocardiographic monitoring system in patients with ST-elevated myocardial infarction. REC CardioClinics, 56(3). 160-167. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rccl.2020.07.005
- Collinson, P. O., & Gaze, D. C. (2020). Point-of-care cardiac markers in the emergency department: a critical review. Clin Chim Acta, 510, 318–324.
- Roche Diagnostics. (2025, September 29). TROP T sensitive rapid assay — intended use and method sheet. Manufacturer document. https://diagnostics.roche.com/
- Mohammadinejad, A., Nooranian, S., Kazemi Oskuee, R., Mirzaei, S., Aleyaghoob, G., Zarrabi, A., Selda Gunduz, E., Nuri Ertas, Y., & Sheikh Beig Goharrizi, M. A. (2024). Development of Lateral Flow Assays for Rapid Detection of Troponin I: A Review. Crit Rev Anal Chem, 54(7), 1936-1950. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408347.2022.2144995
- Moxham, R. N., d’Entremont, M. A., Mir, H., Schwalm, J. D., Natarajan, M. K., & Jolly, S. S. (2024). Effect of prehospital digital ECG transmission on Revascularization Delays and Mortality in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. CJC Open, 9(6), 1199-1206. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjco.2024.06.012
- Byrne, R. A., Rossello, X., Coughlan, J. J., Barbato, E., Berry, C., Chieffo, A., Claeys, M. J., Dan, G. A., Dweck, M. R., Galbraith, M., Gilard, M., Hinterbuchner, L., Jankowska, E. A., Jüni, P., Kimura, T., Kunadian, V., Leosdottir, M., Lorusso, R., Pedretti, R. F. E…ESC Scientific Document Group. (2023). 2023 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J, 44(38), 3720– 3826. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehad191
- Gulati, M., Levy, P. D., Mukherjee, D., Amsterdam, E., Bhatt, D. L., Birtcher, K. K., Blankstein, R., Boyd, J., Bullock-Palmer, R. P., Conejo, T., Diercks, D. B., Gentile, F., Greenwood, J. P., Hess, E. P., Hollenberg, S. M., Jaber, W. A., Jneid, H., Joglar, J. A., Morrow, D. A…Shaw, L. J. (2021). 2021 AHA/ACC/ASE/CHEST/SAEM/SCCT/SCMR Guideline for the Evaluation and Diagnosis of Chest Pain: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation, 144(22), e368– e454. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000001029
- AliveCor, Inc. (2025, Sep 29). KardiaMobile 6L — User Manual (AC-019). https://www.alivecor.com/
- Accu-Tell Troponin I/T Rapid Test — Instructions for Use. Manufacturer document. https://accutell.com/
- ISIS-2 (Second International Study of Infarct Survival). (1988). Collaborative Group. Randomised trial of intravenous streptokinase, oral aspirin, both, or neither among 17,187 cases of suspected acute myocardial infarction. Lancet, 2(8607), 349-360. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2899772/
- Seppälä, H., Klaukka, T., Vuopio-Varkila, J., Muotiala, A., Helenius, H., Lager, K., & Huovinen, P. (1997). The effect of changes in the consumption of macrolide antibiotics on erythromycin resistance in group A streptococci in Finland. Finnish Study Group for Antimicrobial Resistance. N Engl J Med, 337(7), 441-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199708143370701
- Antman, E. M., McCabe, C. H., Gurfinkel, E. P., Turpie, A. G., Bernink, P. J., Salein, D., Bayes De Luna, A., Fox, K., Lablanche, J. M., Radley, D., Premmereur, J., & Braunwald, E. (1999). Enoxaparin prevents death and cardiac ischemic events in unstable angina/non-Q-wave myocardial infarction. Results of the thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) 11B trial. Circulation, 100(15), 1593-1601. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.100.15.1593
Table 1: Feature comparison between smartphone ECG (KardiaMobile) and rapid LFIA troponin tests
| Feature | KardiaMobile ECG (Smartphone) | Troponin LFIA (Rapid Cassette) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary output | ECG tracing (1–6 leads depending on model/placement); visual ST-segment assessment | Qualitative / semi-quantitative cTnI/cTnT (above fixed cut-off) |
| Time to result | Acquisition in ~30–120 s | 10–15 min from sample |
| Setting | Anywhere; handheld; no consumables | Anywhere; no instrument; single-use cassette |
| Diagnostic strength | Early recognition of ST-elevation / ischemia pattern | Biomarker evidence of myocardial injury (less sensitive early) |
| Limitations | Single-lead or limited leads; requires proper placement/interpretation | Lower sensitivity for very early presenters; no precise concentration |
| Best use | Immediate triage; prehospital activation | Corroboration of ACS suspicion; triage where lab not available |
Table 2: Illustrative time metrics (minutes) for POCT pathway (KM + LFIA) vs hospital-only pathway
| Pathway Step | POCT Pathway (KM + LFIA) | Hospital-Only Pathway |
|---|---|---|
| Symptom onset → First ECG | 2–5 (on scene KM) | 30–60 (travel + triage) |
| First ECG → Troponin result | 10–15 (LFIA bedside) | 30–90 (arrival, sampling, lab/queue) |
| First medical contact → Activation decision | ≤15 (ECG + LFIA combined) | 60–120 (ECG, labs, decision) |
Figure 1: Illustrative time to key milestones from symptom onset for two pathways